Copy trading changes how people trade on the stock market by instantly copying the trades of experienced investors, called “signal providers.” It lets new traders benefit from the knowledge of more experienced traders without doing much market research.
With copy trading, users can find many successful traders, examine their trading methods and performance measures, and decide how much money to invest in copying their trades.
However, it’s important to be aware of the risks that come with copy trading, such as market instability, problems with liquidity, and relying on the success of a few traders.
What is Copy Trading?
Copy trading lets buyers use the experience of more experienced traders to make money by copying their trades. New traders can learn from many successful traders on copy trading sites, making their tactics and trading records clear.
This method works especially well for new buyers who don’t have the time or information to devise their trade tactics. It’s common to trade this way for short-term positions, like in swing and day trading, and it focuses on different assets, such as currencies, stocks, and sensitive instruments.
It is possible to make money with copy trading, but buyers should be aware of the risks, such as the unstable market and relying on the success of a few traders.
Copy Trading Example
For example, Investor A, who has little experience trading, can give some of their money to copy Trader X, who has always made good trades.
Investor A, for example, sets aside $1,000 to copy famous dealer X. While Trader X is trading, Investor A’s account makes the same move, buying 50 shares of Company Y at the same price.
Don’t Miss Reading: Have you ever wondered about the mysterious dance of the market, where values rise, fall, or seem to linger in a holding pattern? If you want to understand the language of financial markets, you need to understand the concepts of market behavior, which include uptrends, downtrends, and range markets.
What Are the Most Important Parts of Copy Trading?
There are two people involved in copy-selling.
- Provider: An experienced trader trusted to look at the market and find profitable trading chances is also called a signal provider. They trade based on their ideas, which other traders then copy.
- Copier: A user who keeps up with a signal or service. Instead, they use their trading accounts to copy the provider’s trades. You can do the transaction by hand or use automated trade tools to do it for you.
Suggest To Read: Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines on a price chart used in technical analysis to identify potential support or resistance levels in a financial market. These levels are based on key mathematical ratios derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
How Copy Trading Works? 8 Steps
Here’s how copy trading works:
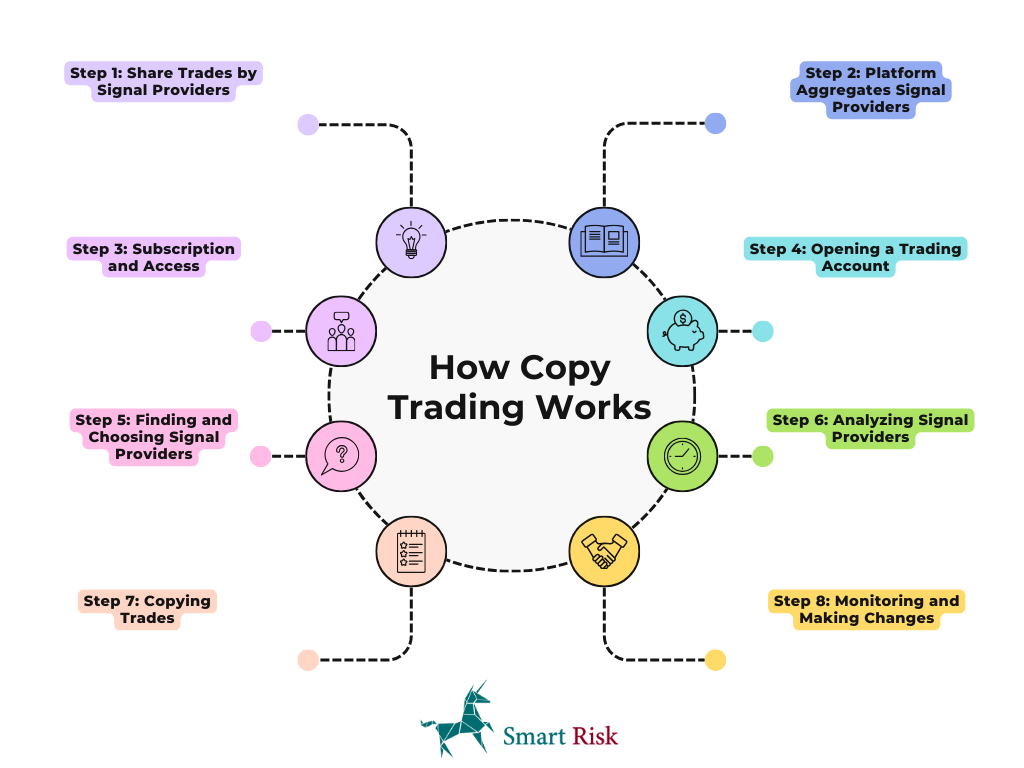
Step 1: Share Trades by Signal Providers
Some of the most experienced traders, called “signal providers,” connect a copy trading tool to a part of their trading accounts or assets. They let other people see their trades right away.
Step 2: Platform Aggregates Signal Providers
Sites that let you copy trades find signal makers willing to share their trades. The service might be free on these sites, or you might have to pay to get to some companies.
Step 3: Subscription and Access
Copier enthusiasts who are new to trading pay to follow the trading methods of tip sources. Once they sign up, copiers can access the signal provider’s trading account and see what they’re doing in real-time on the market.
Step 4: Opening a Trading Account
Market copyers need to open a trading account with a company that gives them access to a copy trading tool, like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5).
Step 5: Finding and Choosing Signal Providers
Copiers look for and choose signal providers based on how they like to trade and what they want to achieve. Many traders have a way to rate signal providers based on how well they’ve done in the past. The site gives more weight to providers with a history of making good deals.
Step 6: Analyzing Signal Providers
Copiers analyze signal providers based on several factors, such as the number of trades they make, the results of those trades, the trading method they use, and the currencies they trade. They may also look at other information the site gives them, like the amount of danger and how often trades happen.
Step 7: Copying Trades
Once a signal provider has been chosen, users can choose to have their trades copied immediately. If the signal source makes a trade, the copier’s account instantly makes the same trade based on the amount of money they were given to spend.
Step 8: Monitoring and Making Changes
Copiers constantly check how well signal providers are doing and may change their payments or the time they are given if performance or market conditions change.
Watch The Videos: Best Trading View Indicators for Price Action & ICT
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Of Copy Trading
| Advantages of Copy Trading | Disadvantages of Copy Trading |
| Copiers can adjust trade sizes according to their account balance. | Selecting the right trader requires thorough research beyond just looking at returns. |
| Allows trading alongside top traders, even for those with limited time. | Copiers may face losses if the trader struggles to adapt to changing market conditions |
| The performance of signal providers is visible | Some providers may charge subscription fees for copying trades. |
| Copiers can diversify their portfolios | Copy trading doesn’t protect against typical market risks |
Advantages of Copy Trading
Here are some key advantages of copy trading:
Flexibility
Although copy trading only involves copying the provider’s trades, the copier decides how much to risk on each trade. For instance, if the provider trades big lots but the copy seller doesn’t have enough money, they can change the trade amount to fit their account balance.
Efficiency
Becoming a successful trader takes a long time; not all traders have time to prioritize this daily. One way to trade like a pro, even when busy, is to use copy trading. Just make sure you set up and monitor your risk limits.
Transparency
Copy trading is similar to social trading in that a scoreboard shows how well different providers are doing. In other words, wins and losses can be seen.
Diversification
The benefits of copy trading extend beyond those traders too busy to engage in active trading. Traders can also copy other traders to spread their risk. You might feel most comfortable with a swing trading approach, but you could copy someone who has done well with short-term trade. Copy trading might help if your strategy isn’t working or you can’t find enough trade chances.
Learn More About Forex: Money and risk management in trading involves employing strategies to safeguard capital and minimize potential losses. This is particularly crucial in dynamic financial markets where volatility can lead to rapid price changes.
Disadvantages of Copy Trading
Here are four negative outcomes of copy trading:
1- Choosing the Right Trader Can Be Hard
If you’re considering buying a stock or an investment fund, you should do the same study to ensure you make the right choice when picking which trades to copy.
Traders with the best monthly gain aren’t always the ones you should copy. There are always more things to consider, like the trader’s greatest loss and how long they’ve been trading.
2- Recognised Danger
Copy trading can be dangerous because losses are copied along with wins. You can change the risk by setting the risk level and how much money you put into your trading account.
However, you can’t change the moves of the trader you are checking out. If the market changes, the master trader might not be able to adjust well, or they might be stressed out and unable to keep their feelings in check while trading. You should consider these things even though you can’t change them.
Suggest To Read: The MACD indicator is widely used in stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies. It helps traders identify crucial market trends, including divergences, crossovers, and overbought/oversold conditions.
Mirror Trading vs Copy Trading: What Are the Differences?
Mirror trading means copying another trader’s full trading plan, which includes using their tools and past trading data. After learning how great traders do it, investors eagerly copy their deals.
On the other hand, copy trading grew out of mirror trading, but it is unclear to investors because they just copy other people’s moves without understanding the strategy behind them.
Mirror Trading and Copy Trading Comparison
- Transparency: Mirror trading is more open because investors can see the whole trading strategy. On the other hand, copy trading is less open because investors can’t see the strategy behind it.
- Control: Mirror trading gives investors more control over their investments because they can look at the trading strategy and make smart choices. On the other hand, copy trading means simply following other people’s trades without understanding the strategy.
- Risk: Both copy trading and mirror trading come with risks. However, investors may better control their risks with mirror trading because they can look at the plan and change how they do things based on what they find. When people copy another trader, they depend more on that trader’s success.
Time To Read: Harmonic patterns in trading have become indispensable tools for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets. These patterns, rooted in the principles of technical analysis and Fibonacci ratios, offer a unique perspective on potential trend reversals.
What Are Copy Trading Risks?
Copy trading offers several benefits, but it also comes with certain risks, such as any investment strategy.

1- Dangers in the Market
Market risk is the chance of losing money because the prices of securities go up and down. Traders aim to make money when an asset’s value goes up, but there is always the chance that an asset will lose value.
Mitigation includes:
- Trading tactics.
- Diversification investments over a range of assets
- Asset allocation techniques to protect against large losses resulting from unfavorable market movements
2- Risk of Liquidity
Traders face liquidity risk when they can’t get out of trades at the amounts they expected. Evaluating a strategy’s past success, especially its biggest loss, can help you understand how much you might lose.
It’s also important to know how liquid the traded items are since different assets have different amounts of liquidity, affecting how easy it is to exit a situation.
3- Systematic Risk
This type of risk is related to bigger market problems that affect all businesses, like wars or economic crises. Emerging market currencies are especially vulnerable to these threats, which could cause capital lockdowns.
Trading methods must consider global events, even though they don’t happen often.
4- Risks in Operations
These risks come from internal systems, processes, or mistakes people make, which could result in losses. Mistakes in trade processing or problems with the software can cause business risks in copy trading.
Keeping an eye on the copy trading platform’s dependability and safety and regular talks with the copy trader can help lower these risks.
5- Concerning Counterparty Risk
This is the chance that the other party in a trade will not meet their responsibilities. This could show up in copy trading if the copied seller doesn’t make trades correctly or handles money badly.
Don’t Miss Reading: Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a trading approach used to spot price variations in the market, which are indicated by distinct candlestick patterns and gaps in the price history on charts.
Top 7 Copy Trading Terminology
Copy trading vocabulary includes the language and words used in copy trading systems to talk about different parts of the process, such as signal providers, followers, and performance metrics.
- Copying Ratio: The amount of a follower’s capital committed to copying a strategy provider. For instance, if a follower gives $1,000 to copy a strategy provider with a 50% copying ratio, the follower will use $500 to copy the provider’s moves.
- Profit/Loss Percentage: The number that shows how much money a trade or the whole stock made or lost. In this case, a profit ratio of 10% means that a trade made a profit of $100 on an investment of $1,000.
- Fixed Size: When you use fixed-size copying, you choose the total size of the trade you want to make, not the spot size of the signal. A fixed size of $500 means that your copy trade will always be $500, even if the signal buys two shares of a stock.
- Mirror Master Size: When you copy in mirror master size, you directly copy the size of the signal’s position. For example, if the signal buys £50 worth of gold, then picking mirror master size will also buy £50 worth of gold.
- Mirror Master Risk: This risk changes your trade size based on your account size. This way, you take the same risk as the signal you’re copying. Let’s say the signal risks 5% of their account on a trade. If you have a $10,000 account, mirror master risk will copy a trade that risks $500.
- Max Drawdown: The greatest loss seen from peak to dip before a new peak is reached is called max decline. You can’t copy when your account’s value drops below $7,000. This happens if your account has a 30% maximum decline and its highest point value is $10,000.
- Level of Warning: You will be notified when your loss hits the warning level you set. Say you set the warning level to 20%, and your account’s loss hits 20%; you’ll get a message.
Can You Make Money by Copy Trading?
It is possible to make a lot of money with copy trading if the chosen seller does well, but it’s important to be aware of the risks. Market risk, in which bad tactics can result in losses, is still a major issue.
Liquidity risk can also be difficult to manage when the market is unstable, which could affect trade completion. However, copy trading can still be effective if you research, spread risk, and use risk management tools.
Investors can lower these risks by choosing skilled traders with a history of making money. This makes copy trading possible to make money in the financial markets.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Mirror and copy trading are both ways to trade, but they differ. When you mirror trade, you do exactly what the master trader does, right down to the size of the position they open on each trade. You use the same trading technique and make the same trades as the signal provider when you copy trade, but you can change the size of your positions, which is very important.
Like all other types of trading, copy trading comes with some risk. However, you have full power over your account and can change the risk factors to fit your needs. You must always research, even if you are following another trader.
You can start copy trading with any amount of money. Even though you can start with as little as $100, you may not have as many options with that much money.
Yes, most copy trading platforms let you pick the strategy provider that best fits your financial goals with the help of tools and filters. You can choose based on revenue, risk level, number of followers, and total funds managed.
No, one of the benefits of copy trading is that it lets buyers make money in the stock market even if they have never traded before. By copying the trades of more experienced traders, you might get the same results without making your own trading choices.

